 in C programming?" width="700" height="622" />
in C programming?" width="700" height="622" />A function is a block of code that performs a specific task.
Suppose, you need to create a program to create a circle and color it. You can create two functions to solve this problem:
Dividing a complex problem into smaller chunks makes our program easy to understand and reuse.
There are two types of function in C programming:
The standard library functions are built-in functions in C programming.
These functions are defined in header files. For example,
You can also create functions as per your need. Such functions created by the user are known as user-defined functions.
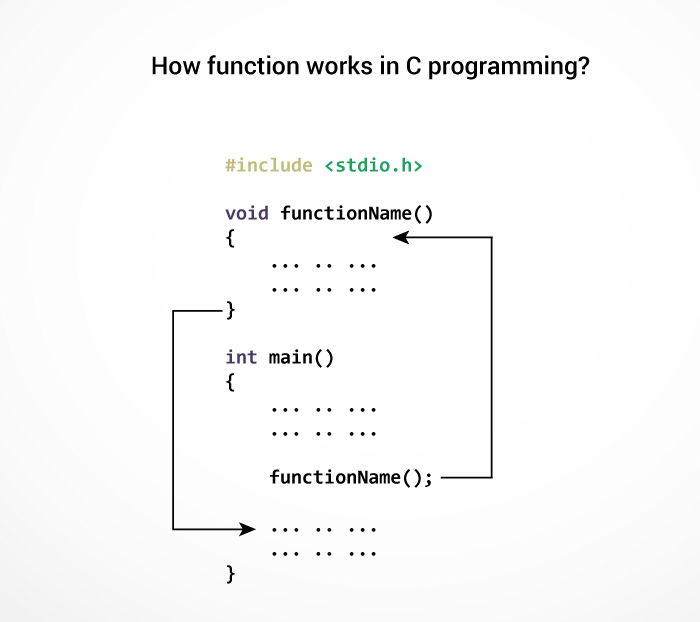
The execution of a C program begins from the main() function.
When the compiler encounters functionName(); , control of the program jumps to
void functionName()
And, the compiler starts executing the codes inside functionName() .
The control of the program jumps back to the main() function once code inside the function definition is executed.
 in C programming?" width="700" height="622" />
in C programming?" width="700" height="622" />
Note, function names are identifiers and should be unique.
This is just an overview of user-defined functions. Visit these pages to learn more on: